Material That Transfers Heat Well
Which Metals Dissipate Estrus the Best
Some metals dissipate heat more effectively than others, and this thermal conductivity is essential in a range of applications. Thermal electrical conductivity is the measure of a metallic's ability to acquit rut. What this means is that that the metal acts to cool temperatures, through a procedure of dissipation.
The metals with the highest thermal conductivity are copper and aluminium. The everyman are steel and bronze.
Metals that conduct rut finer are used in applications where transferring estrus is essential, either as part of a cooling or heating procedure. On the other paw, metals similar steel, which is a poor usher of heat, are suitable for loftier temperature environments where rut resistance is crucial.
For case, as an effective oestrus conductor, copper is used in heating rods and wires, hot h2o tanks and heat exchangers. Similarly, aluminium alloys are the most common textile in heat sinks.
Where heat resistance is an essential function, then metals with a low thermal conductivity are most appropriate, for example, aeroplane engines fabricated of steel.
In thermal electrical conductivity applications, these metals must first be manufactured to make them suitable for their end purpose. This is why high temperature insulation and furnace prophylactic systems are crucial for the foundry and steel industry.
Heat Exchangers
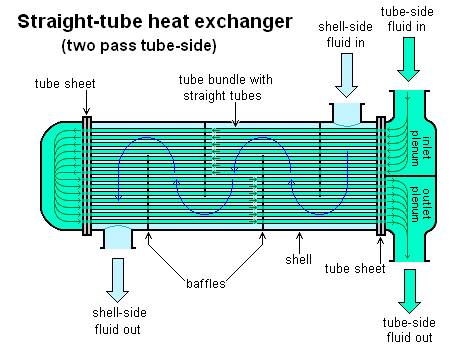
Heat exchangers are devices that transfer heat from ane course to some other. This exchange of matter might be a fluid, such as oil or h2o, or moving air. The main metal in rut exchangers is copper, but aluminium can provide a cost-effective alternative in some applications. Both are used because they bear rut well.
A mutual blazon of heat exchanger is the car radiator. This engine coolant is made from layers of metal sheets stacked together, with an aluminium core.
It cools the engine past circulating a liquid h2o or oil-based coolant. This liquid is heated through the engine block, and so loses its heat through the radiator before being returned to the engine.
-Heat exchangers are also used in shipping engines to remove excess heat, and in military equipment, lasers, ten-rays and power supplies.
-Industrial facilities that utilise oestrus exchangers include nuclear power plants and chemic plants. Typically this involves copper-nickel alloy tubing, with a good resistance to corrosion.
-Gas water estrus exchangers transfer heat generated by gas fuels to h2o in residential and commercial boilers.
-Evaporator units drive air-to-air heat exchange in air-based heat pumps used in domestic and commercial heating systems.
Heat Sinks
These are a special grade of estrus exchanger reliant on thermal conductivity to transfer heat generated past electronic or mechanical devices into a moving coolant fluid, which then transfers heat away to cool.
Again, these use metals with a high thermal electrical conductivity.
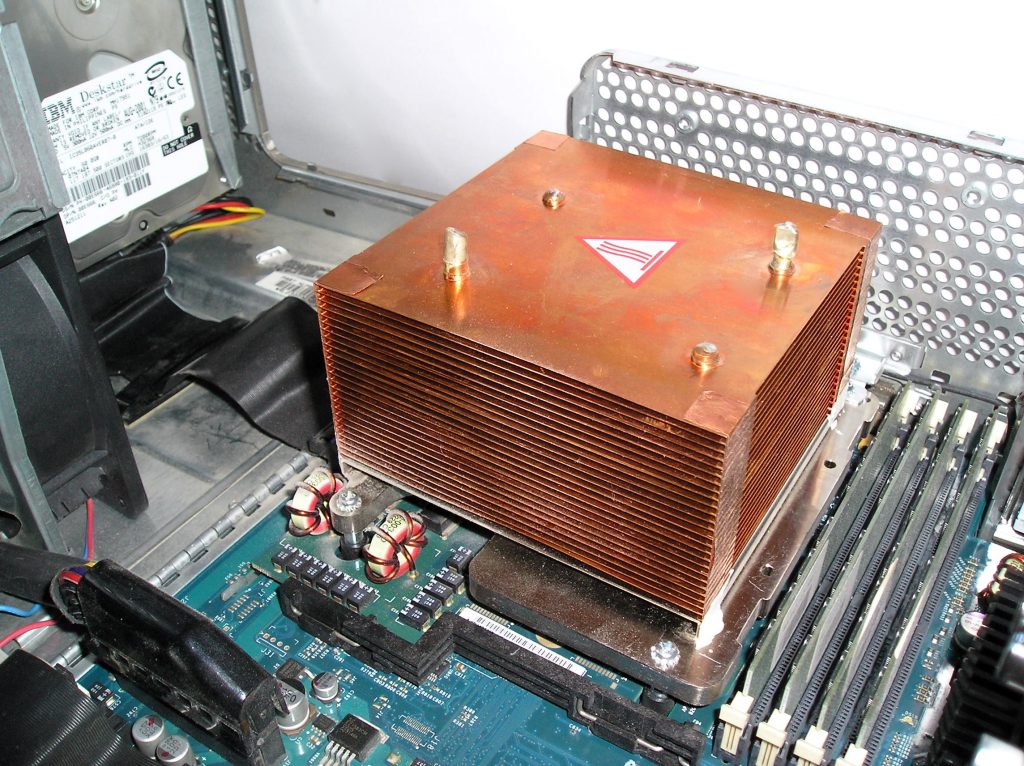

Heat sinks are usually made from aluminium alloy, which has one of the highest thermal conductivity values. They are used in semiconductors for a variety of consumer and industrial electronics.
Computers use heat sinks to cool fundamental processing units and graphics processors, but y'all volition also notice them in ability transistors and LEDs.
Perhaps a more than hands recognisable application of thermal electrical conductivity, cartoon on heat dissipation qualities, is cookware. Loftier-quality pans take copper bottoms because this will comport the oestrus rapidly, spreading it evenly beyond the surface.
Aluminium and Copper Smelting Processes
As thermally conductive metals, copper and aluminium are of huge applied value. However, the smelting process to excerpt these metals from their ores itself requires expert thermal management.
Induction furnaces normally process copper and aluminium, which accept a high melting temperature of 1084°C and 660°C respectively. This induction heating is cleaner and more energy-efficient than traditional methods, but it requires precise temperature command and thermal management.
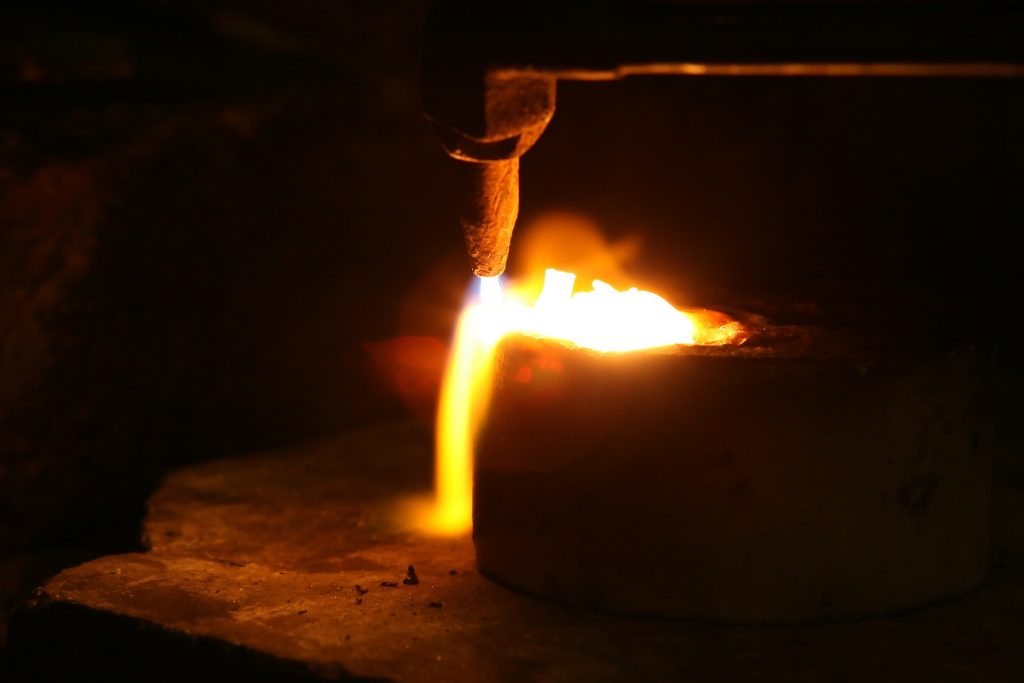

Induction furnaces do not accept a refining capacity, so the materials they process must first exist clean of any oxidation products. These furnaces tin be either coreless, or have a molten metal loop winding through an atomic number 26 core.
Insulation and Furnace Safety
Just as copper and aluminium are used in estrus transfer, and so this process aids the bodily product of these metals in the first identify. Microporous high temperature insulation helps forbid heat transfer in furnaces smelting these metals.
Elmelin's microporous material is chosen Elmtherm, and it comes in several grades. In Aluminium launder systems it optimises motion and minimises heat loss; and in melting furnaces it helps maintain even heat distribution and the quality of the finished production.
Some other aspect of copper and aluminium smelting is ensuring furnace safety. Vapourshield is specially effective in controlling emissions when melting downwards copper alloys which have different chemical components.
Supporting Thermal Conductivity
Elmelin supports a broad range of industries that rely on heat transfer processes using thermally conductive metals that dissipate estrus. Nosotros also provide essential loftier temperature insulation for foundries that process these metals. For more than data, delight call us on +44 20 8520 2248, email sales@elmelin.com, or complete our online inquiry form. We'll get back to you as shortly every bit possible.
Material That Transfers Heat Well,
Source: https://elmelin.com/which-metals-dissipate-heat-the-best/
Posted by: jacobsthujered.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Material That Transfers Heat Well"
Post a Comment